Earth Observations are Essential to Sustainability on Earth
Earth observations are essential to sustainability on Earth. We use observations from satellite to support sustainable development efforts related to water allocations, food security, water quality, air quality, biodiversity conservation, natural resource management like timber and minerals, shipping and navigation, as well as disaster response and resilience. In fact, these observations are so valuable that the World Economic Forum predicts that their value will be over $700 Billion (USD) by 2030.
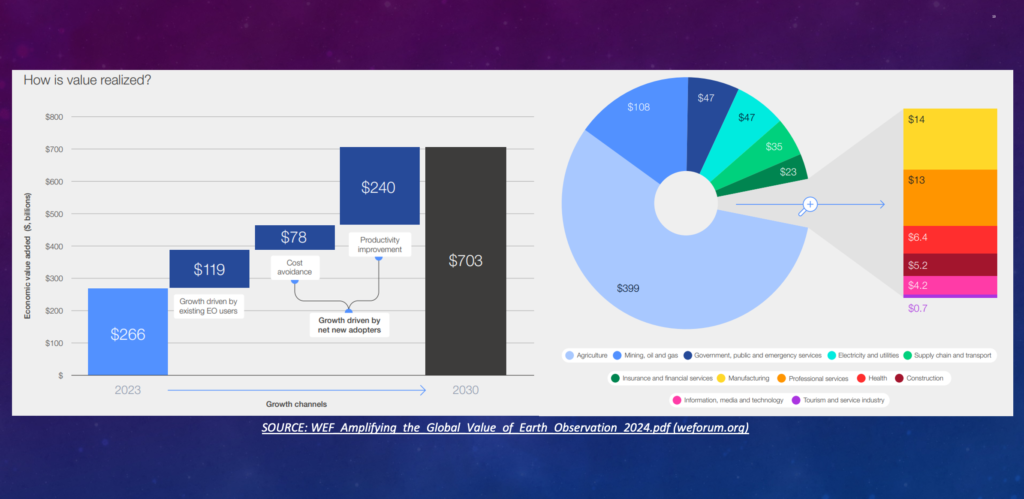
While the value of these observations is well recognized, the resistance to funding sustained and new observations is really more about how they are funded. Congressional budgets are flat (at best), so how do we cover the extra cost to realize the full value of sustained and new observations?
Despite the same objective to provide sustained and new Earth Observations, different sectors often compete rather than collaborate. The fundamental problem is that the current financing model creates a zero-sum game – when one sector gains, the others lose.
The systems are failing...
The pursuit of sustainability through Earth observations is increasingly challenged by the realities of climate change. While innovative aerospace technologies offer valuable data, they must be balanced against their environmental impact to truly contribute to sustainability efforts. Ensuring that these observations do not inadvertently compromise ecological integrity is crucial for fostering a resilient future. Thus, a comprehensive approach that prioritizes both innovation and environmental stewardship is essential.
There is no question that the value of new and sustained Earth observations from space is growing. Despite growing demand, the challenge presents that US congressional appropriations funding Earth observations are relatively static. Several models exist for financing Earth observations by capitalizing on the value that the observations provide; however barriers limit the ability of those new models to support the growing needs.
Now is the Time to Change the US Civil Space Economy
Earth’s Space Future, an effort to gather and synthesize information on enablers and inhibitors of cross-sector collaboration to support sustained and new Earth observations. This cross-sector alliance will recommend to the broader Earth observations enterprise next steps for creating sustainable and effective business models. To start, the alliance will host a community workshop bringing together procurement specialists, aerospace finance experts, business development strategists, and decision makers. The workshop will analyze different business models via table-top exercises to identify inhibitors, enablers, and applicability of different models to meet the varying functional needs for supporting new and sustained Earth observations.
The mid-term Earth Science Decadal Survey called for a need to develop a continuity framework amidst congressional budget challenges. The 2024 National Plan for Civil Earth observations Initiative A aims to ensure sustained and monitoring system capacity, recognizing Earth observations as infrastructure “needed over long timescales including continuity with historical data. Finally, a recent report, requested by Congress in the CHIPS and Science Act of 2022, evaluated NASA’s current workforce, infrastructure, technological capabilities, and their interfaces for meeting their strategic goals. The report concludes that NASA is at a crossroads, marking a pivotal time to re-evaluate NASA’s role in maintaining global leadership for space exploration.
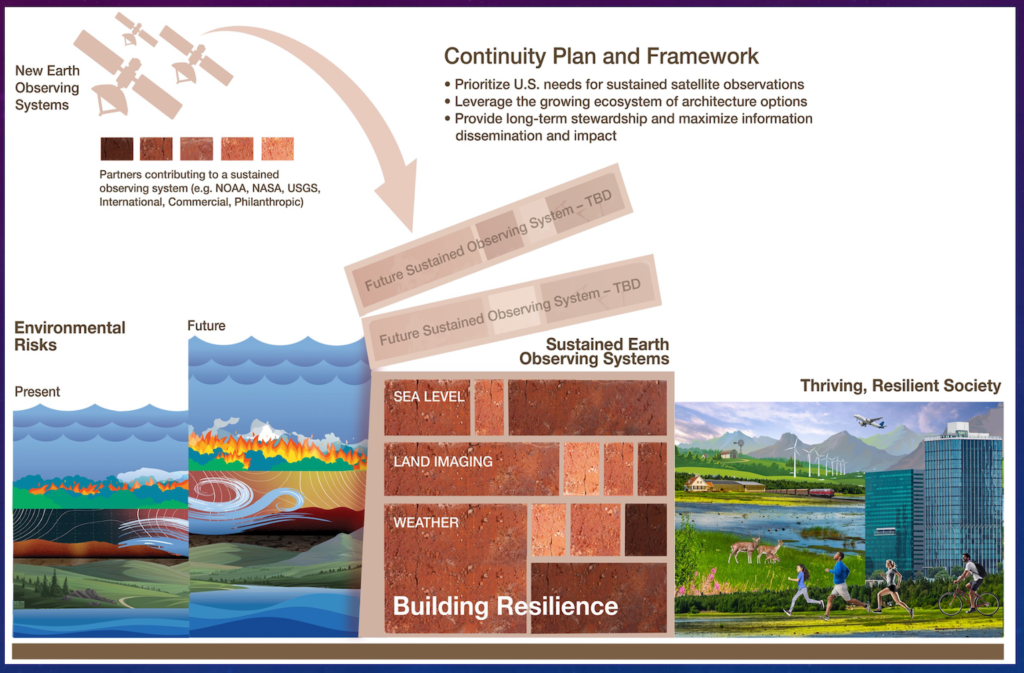
NASA's Investment
Earth’s Space Future contributes to NASA 2022 Strategic Plan to catalyze economic growth and drive innovation to address National challenges, and Strategic Goal 4 to enhance capabilities and operations to catalyze current and future missions. Because the landscape of participants and stakeholders in Earth observations is rapidly changing, NASA Earth Science Division is well positioned to bring together the breadth of expertise from across public and private sectors to assess novel architectures for sustained and new observations. In this context, mission architecture encapsulates the mission system including people, funding, software, hardware, interactions and processes spanning organizations.
A Sustainable Earth Space Future
WKID Solutions, Narayn Strategy, and KnowInnovation partner together to lead Earth’s Space Future, a funded NASA’s Topical Workshops, Symposiums, and Conferences in Space and Earth Science and Technology.
Using WKID Innovation, Earth’s Space Future will produce a synthesis report documenting inhibitors and enablers for a viable and effective business model to support sustained and new Earth observations that can support the science and decision-support needs of the US. Inhibitors and enablers include:
- Policy factors include partnering administration, contracts, acquisition and Statutory Authorities, interagency and international working agreements, regulatory and national security, and open, transparent, trustworthy data.
- Economic factors include phased funding, revenue generation, the interagency aerospace financing (e.g., Joint Space Cost Council), acquisition models, and research and development incentives.
- Sociocultural factors include workforce present and future, knowledge management, national priority setting, and interagency and cross-sector details.
- Technological factors include long-lead development transition plans for short-term iterative improvements, agility to fail fast, risk tolerance, and pre-competitive spaces.
The Earth’s Space Future effort seeks to synthesize many different national reports and plans, and brings the US Earth Observing Enterprise together to synthesize common inhibitors and enablers for supporting both sustained and new Earth observations. By systematically and strategically co-creating with change agents across sectors, a series of influential byproducts are expected.
